- Beauty
We humans have never lacked imagination, and when we have nothing to do, we often think of some strange and weird questions, such as the one raised by someone: How long after the sun goes out will humans notice it?

Although it is unlikely to happen, this has not dampened the enthusiasm for the discussion, with one view suggesting that it would take about 8 minutes, and another suggesting that humans would not notice it until at least 10,000 years later. So is it 8 minutes or 10,000 years?
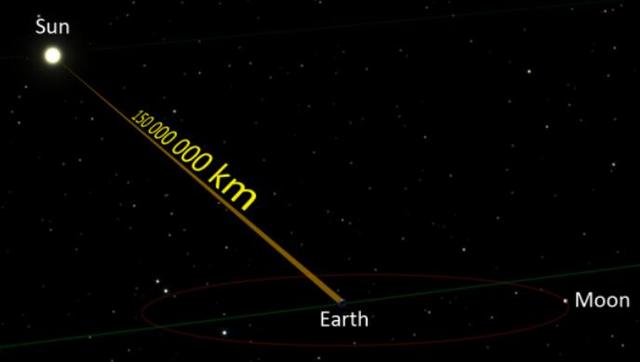
The first view is well understood. The average distance between the earth and the sun is about 150 million kilometres and the speed of light in a vacuum is about 300,000 kilometres per second, while the cosmic space between the earth and the sun can be regarded as a vacuum. A simple calculation shows that it takes 8 minutes and 20 seconds for the light from the sun to reach the earth, so it can be said that about 8 minutes after the sun goes out, humans will be able to notice it.
The second view is based on the principle of solar luminosity, which suggests that the sun is not a fireball burning as a whole. This means that only after the last energy released before the sun went out was transmitted to the surface of the sun would the sun appear to change and thus be perceived by humans.
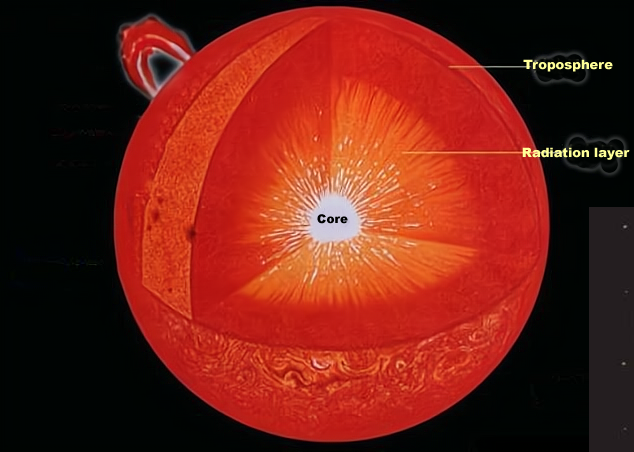
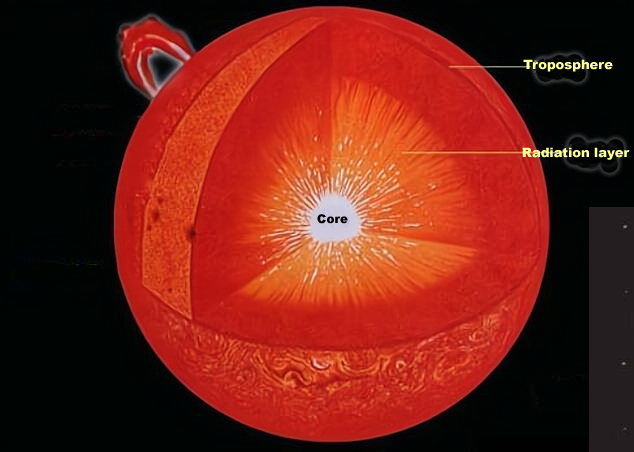
As the diagram above shows, the interior of the sun is divided into a core, a radiation zone and a troposphere, with nuclear fusion occurring only in the core, where the light released is gamma rays (i.e. Electromagnetic photons with frequencies above 1.5 gigahertz and wavelengths shorter than 0.01 angstroms). The radius of the sun is about 6.955 x 10^5 km and these photons travel at the speed of light and would have covered this distance in only 2.3 seconds, however, in the interior of the sun, these photons cannot travel in a straight line.
The density of the sun increases gradually from the outside to the inside, and in the core of the sun the matter density is already 150 g/cm3, which means that the photons, in such a dense environment, keep hitting other particles, so much so that the average free range of photons inside the sun is only about 0.1 mm to 1 cm, meaning that for every 0.1 mm to 1 cm the photon advances, it collides with another particle .
When a collision occurs, the photon may be bounced off, its direction of travel may change randomly, or it may be absorbed by another particle, which absorbs the photon and enters an excited state, and after it is de-excited, it releases a new photon in a random direction.
In this way, the photons bang around in the sun's interior, and in the process "Old photons are absorbed and new photons are released", so that the energy released by the sun's core takes a very long time to reach the sun's surface. According to scientists, this time is at least 10,000 years.
I believe that you are already a bit skeptical, so does it really take 10,000 years from the time the sun goes out to the time it is "Detected by humans"? No, because this view does not take into account one important factor - the sun's own gravity.
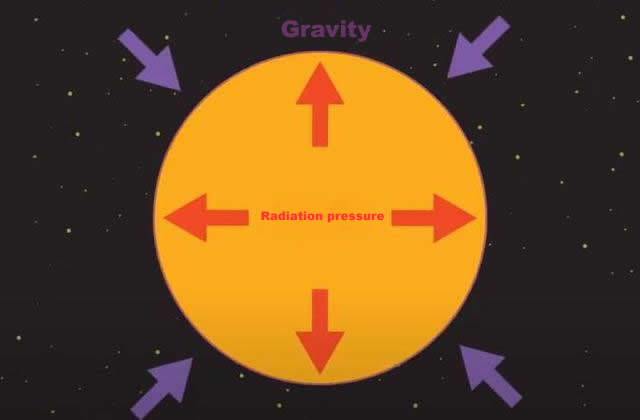
The energy released by the sun's nuclear fusion reactions, apart from making the sun shine and heat up, has an important role to play in resisting its own gravity. It is conceivable that if the sun's fusion reaction were extinguished, its internal source of power to resist gravity would be lost, in which case the sun's own gravity would prevail, causing the sun to slowly collapse.
The extent of the collapse depends on the amount of energy remaining inside the sun, as shown by a certain degree of contraction in the sun's volume for each point of energy reduction inside the sun.

As the source of all things on earth, the sun has always been the focus of human observation, with a large number of observation devices watching its every move at every moment. So it is safe to say that this abnormal contraction of the sun would have been detected by humans if only it had taken a little longer than 10,000 years, but of course, that time period would still have to be much longer than 8 minutes.
The good news is that the sun will not collapse into a black hole, nor will it become a neutron star, this is because the sun does not yet have the mass to become a black hole or a neutron star. At a certain point of collapse, the "Electron condensation pressure" Inside the sun will be able to resist its own gravity, and in this state the sun will turn into a white dwarf.